Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Sequence-Based Recommendation Systems
Last Updated: 29th January, 2026Using RNNs, GRUs, and LSTMs
While traditional recommendation models treat user–item interactions as static data, real-world user preferences are highly dynamic and evolve with time, context, and behavior. Sequence-based recommendation systems address this limitation by incorporating the temporal order of interactions — for instance, the exact sequence in which a user watches movies, shops for products, or listens to songs. This ordering provides valuable contextual cues about shifting interests, allowing the system to predict what the user might engage with next.
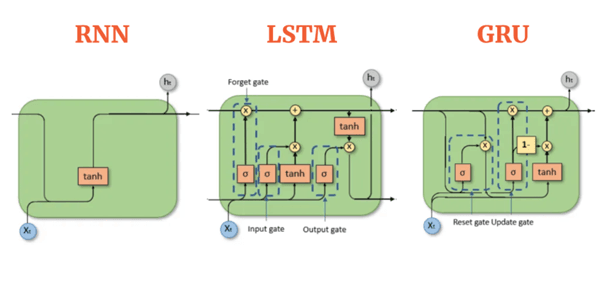
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are naturally suited for sequential data because they maintain a hidden state that captures information from previous time steps. However, standard RNNs often suffer from vanishing gradient problems, limiting their ability to capture long-term dependencies. To overcome this, advanced variants such as Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks introduce gating mechanisms that control how much past information is retained or forgotten. These models can effectively learn long-term behavioral patterns, such as recurring interests or evolving tastes.
For example, in a music streaming app, an LSTM might learn that after listening to several high-energy tracks, a user tends to switch to softer, acoustic music — reflecting a natural mood shift.
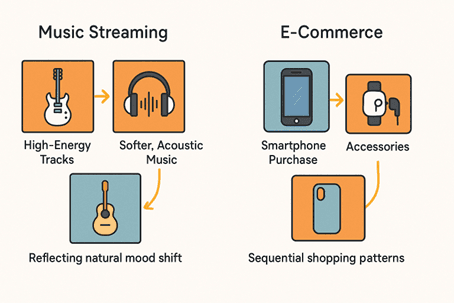
Similarly, in an e-commerce setting, GRUs can capture sequential shopping patterns, such as buying accessories after a smartphone purchase. This temporal modeling enables context-aware, session-based recommendations that adapt not just to who the user is, but also when and how they interact. By leveraging RNNs, GRUs, and LSTMs, modern recommendation systems can evolve continuously, delivering more personalized and timely suggestions that match the user’s current state and intent.
Temporal Recommendations and Next-Item Prediction
Temporal recommendation systems focus on understanding when and in what order users interact with items, enabling them to predict the next likely action or item in a sequence. This sequential awareness is vital for dynamic platforms such as streaming services, online shopping sites, or personalized news feeds, where the timing and order of interactions can reveal deep insights into user intent. Unlike static models that consider only overall preferences, temporal recommenders emphasize short-term interests and session-level behavior, adapting to changing contexts in real time.
Temporal Recommendation System and Next-Item Prediction Example
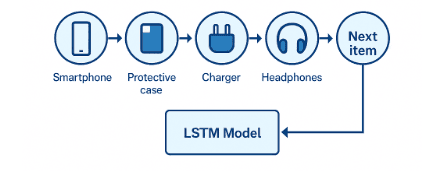
For example, an LSTM-based model trained on e-commerce data might detect that after buying a smartphone, a user often purchases accessories like a case or charger within the next few interactions.
By recognizing such recurring behavioral patterns, the system can proactively suggest these complementary products, improving both user satisfaction and conversion rates. Similarly, in a video streaming platform, the model might recommend the next episode or similar genres based on a user’s recent watch history and time of day.
Modern temporal recommenders often integrate attention mechanisms alongside RNNs, GRUs, or Transformers. The attention layer helps the model focus on the most relevant parts of a user’s history — for instance, prioritizing recent or contextually significant actions over older ones. This not only enhances prediction accuracy but also improves interpretability, as the model can explain why certain items were recommended. By combining sequence modeling with temporal awareness, next-item prediction systems create highly responsive and context-driven recommendation experiences.
Module 3: Deep Learning for Recommendations
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
