Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Introduction to ANN
Last Updated: 2nd February, 2026Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are the foundation of deep learning. They are inspired by how the human brain processes information through interconnected neurons. In an ANN, each artificial “neuron” receives numerical inputs, performs a small computation, and passes the output forward — similar to how biological neurons communicate through electrical signals.
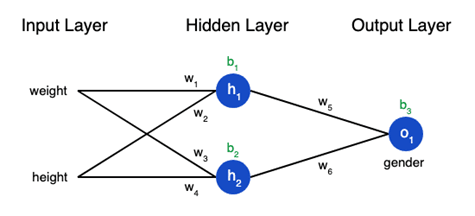
A single artificial neuron performs three key operations:
- Receives inputs — These could be pixel values, numerical features, or outputs from previous layers.
- Applies weights and biases — Each input is multiplied by a weight, and a bias term is added. These parameters determine how important each input is.
- Passes the result through an activation function — This introduces non-linearity, allowing the network to learn complex patterns.
Sends the output to the next layer — Layers are stacked to form a network capable of learning hierarchical patterns.
Example in Python
Input:
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import layers model = keras.Sequential([ layers.Dense(8, activation='relu', input_shape=(4,)), layers.Dense(3, activation='softmax') ]) model.summary()
Output:
Model: "sequential" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= dense (Dense) (None, 8) 40 dense_1 (Dense) (None, 3) 27 ================================================================= Total params: 67 (268.00 Byte) Trainable params: 67 (268.00 Byte) Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte) _________________________________________________________________
From the output, you can see that:
- First Dense Layer:
This layer has 8 neurons and receives 4 input features.
The total parameters are computed as:
(4 × 8) + 8 = 40
The first term represents the weights, and the second term represents the biases. - Second Dense Layer:
This layer has 3 neurons (for 3 output classes).
Total parameters: (8 × 3) + 3 = 27 - Total Trainable Parameters = 67
These are updated during training to reduce the model’s error.
This simple ANN can learn patterns from structured data — such as numbers, tabular data, or basic classification tasks. However, when dealing with high-dimensional inputs like images, where spatial relationships matter, a standard ANN becomes inefficient. This challenge is what led to the development of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which you’ll explore next.
Module 1: Deep Learning Foundations
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI System Design
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
