Free Masterclass on Feb 18
Inside AI Systems: How LLMs Train, Reason & Act
Configuring TLS/SSL
Last Updated: 13th February, 2026Introduction
Imagine sending a sealed envelope through the mail but without actually sealing it. Anyone handling it could peek inside and read the message.
That’s exactly what happens when data travels between your MongoDB server and clients without encryption. Even if your database is protected and encrypted on disk (Encryption at Rest), the data in motion traveling over the network is still vulnerable to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
Encryption in Transit, powered by TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security / Secure Sockets Layer), solves this problem. It ensures that data exchanged between MongoDB and applications is encrypted end-to-end, making it unreadable to attackers intercepting the traffic.
By the End of This Lesson, You’ll Know How To:
Generate and configure TLS/SSL certificates in MongoDB
Enable secure communication between clients and servers
Verify and test SSL connections for MongoDB deployments
Think of it like putting your confidential letter in a tamper-proof envelope that only the sender and receiver can open.
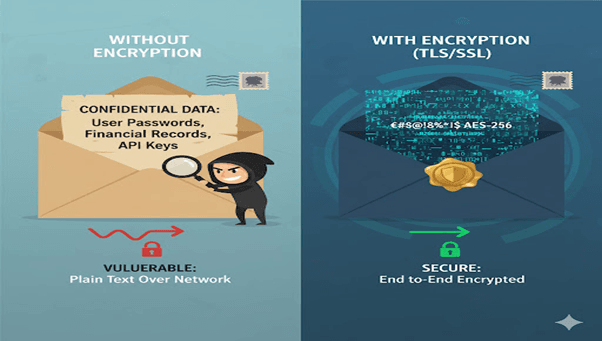
What Is Encryption in Transit?
Encryption in Transit protects data while it moves between:
MongoDB clients ↔ servers
MongoDB replica set members
MongoDB sharded cluster components
It uses TLS (Transport Layer Security) to encrypt this communication so even if packets are intercepted, they can’t be decoded.
Key Takeaway:
Encryption at Rest protects stored data.
Encryption in Transit protects data while it’s being transmitted.
Enabling TLS/SSL in MongoDB
Step 1: Generate Self-Signed Certificates (for Testing)
# Generate private key openssl genrsa -out mongodb.key 4096 # Generate certificate signing request (CSR) openssl req -new -key mongodb.key -out mongodb.csr # Generate self-signed certificate (valid for 365 days) openssl x509 -req -in mongodb.csr -signkey mongodb.key -out mongodb.crt -days 365
Step 2: Combine Key and Certificate
cat mongodb.key mongodb.crt > mongodb.pem
Step 3: Configure MongoDB to Use TLS
Edit your mongod.conf file:
net: ssl: mode: requireSSL PEMKeyFile: /etc/ssl/mongodb.pem CAFile: /etc/ssl/ca.pem
Step 4: Restart MongoDB
sudo systemctl restart mongod
Now, MongoDB will only accept encrypted SSL connections.
Connecting via SSL
Use the Mongo shell to connect securely:
mongo --host yourserver:27017 --ssl --sslCAFile /etc/ssl/ca.pem --sslPEMKeyFile /etc/ssl/mongodb.pem
If successful, your client-server connection is encrypted.
Real-Life Examples
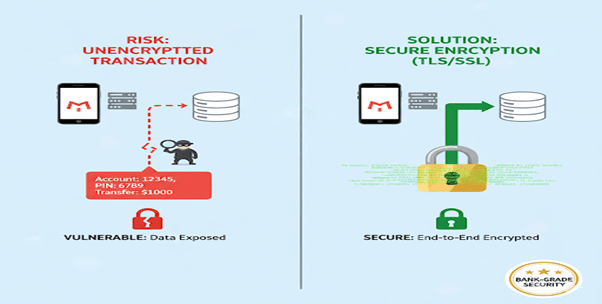
1. Banking Application
Banks use TLS/SSL to protect real-time financial transactions between app servers and MongoDB databases.
Outcome:
Prevents exposure of account details and transaction histories.
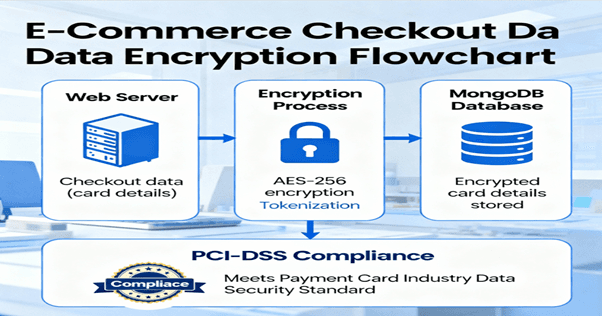
2. E-Commerce Platform
An online store encrypts checkout data transmitted from web servers to MongoDB to secure customer card details and orders.
Outcome:
Ensures compliance with PCI-DSS and boosts user trust.
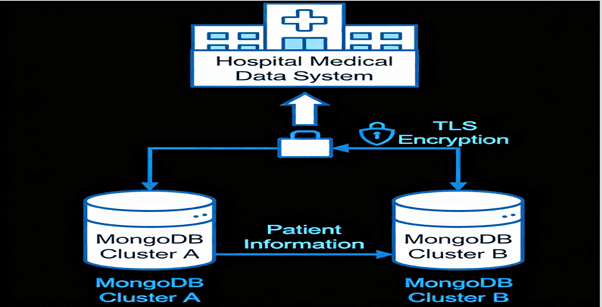
3. Healthcare Systems
A hospital uses TLS to encrypt medical data shared between multiple regional MongoDB clusters.
Outcome:
Safeguards sensitive patient information during data synchronization.
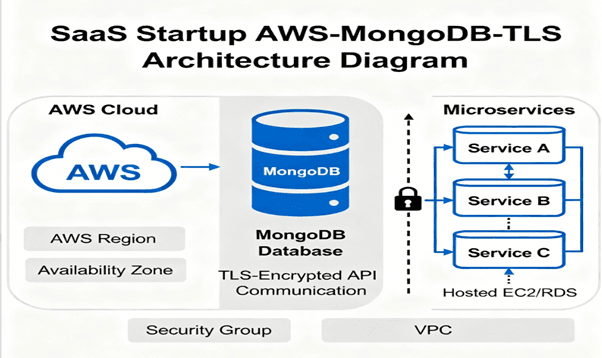
4. Cloud Deployment
A SaaS startup hosting MongoDB on AWS enables TLS to secure API communications across microservices.
Outcome:
Avoids data leakage during inter-service data exchange.
Module 2: Data Encryption Techniques
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI System Design
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
