Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Creating Users and Roles
Last Updated: 13th February, 2026Introduction
Imagine managing a big office building. You wouldn’t give every employee the master key, right?
Instead, you’d issue specific access cards — one for staff, another for managers, and a few master keys for admins.
MongoDB works the same way.
Once authorization is enabled (from Lesson 1), you can define users and roles to control who can access what. This ensures developers, analysts, and admins can all use the same database securely and efficiently — without stepping on each other’s toes.
In This Lesson, You’ll Learn How To:
Create users in MongoDB
Assign built-in roles like read, readWrite, and dbAdmin
Design custom roles for fine-grained control
By the end, you’ll be able to build a role-based access system that keeps your database safe while empowering your team.
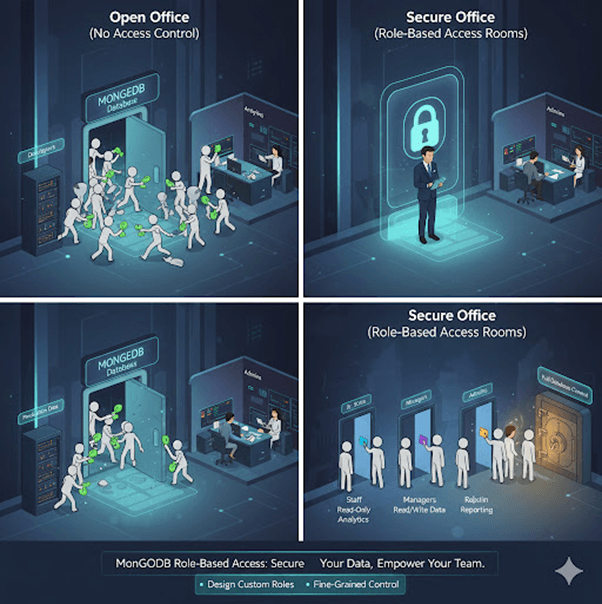
Understanding Users and Roles
Users in MongoDB are defined per database and authenticated with a username and password.
Roles define the level of access a user has — for example, reading data, writing data, managing indexes, or administering users.
MongoDB provides built-in roles for common permissions and also supports custom roles for specific access requirements.
Built-in Roles Overview
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| read | Allows user to read data only |
| readWrite | Allows user to read and write data |
| dbAdmin | Allows user to perform administrative tasks on a database |
| userAdmin | Allows user to create and modify roles and users |
| clusterAdmin | Grants cluster-wide administrative privileges |
Code Examples
1. Create a Read-Only User
use myDatabase db.createUser({ user: "reportViewer", pwd: "StrongPassword@123", roles: [{ role: "read", db: "myDatabase" }] })
This user can only view data in myDatabase.
2. Create a Read/Write Developer User
use myDatabase db.createUser({ user: "developer", pwd: "DevPass@2025", roles: [{ role: "readWrite", db: "myDatabase" }] })
This user can add, update, or delete documents.
3. Create a Database Administrator
use admin db.createUser({ user: "dbAdminUser", pwd: "SecureAdmin#2025", roles: [{ role: "dbAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" }] })
This user can manage indexes, view stats, and modify schemas across databases.
4. Create a Custom Role
You can design a custom role for specialized needs.
use admin db.createRole({ role: "dataAuditor", privileges: [ { resource: { db: "salesDB", collection: "" }, actions: ["find"] } ], roles: [] })
Then assign it to a user:
db.createUser({ user: "auditor", pwd: "Audit@2025", roles: ["dataAuditor"] })
This user can only read from salesDB and nothing else.
Technical Example
Let’s say your team has:
Developers → Need to read and write data
Analysts → Need read-only access
Admins → Need full control
| User | Role | Database | Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| developer | readWrite | projectDB | Read/Write |
| analyst | read | projectDB | Read-only |
| admin | dbAdminAnyDatabase | All | Manage Databases |
This ensures no unauthorized changes or accidental deletions occur.
Real-Life Examples
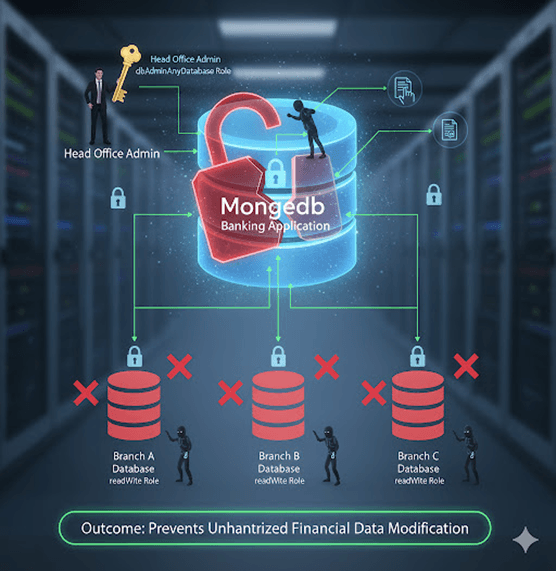
1. Banking Application
Each branch’s system operator gets a readWrite role for their own database but cannot access others.
The head office admin holds a dbAdminAnyDatabase role for overall maintenance.
Outcome: Prevents unauthorized financial data modification.
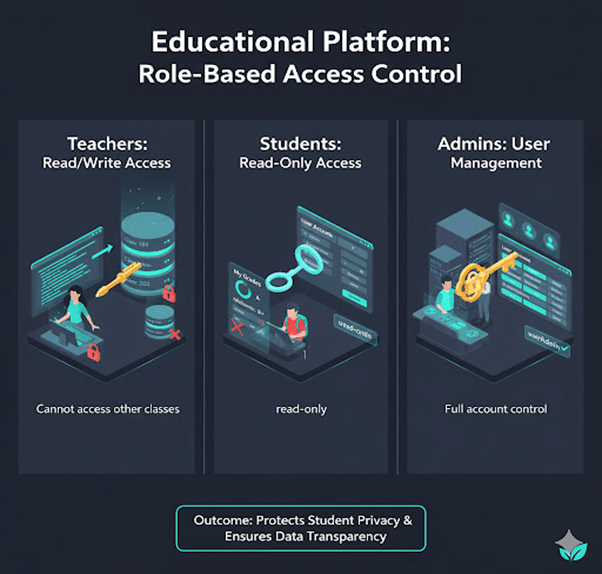
2. Educational Platform
Teachers have readWrite access to their class database.
Students get read-only access to their grades.
System admins have userAdmin access to manage accounts.
Outcome: Protects student privacy and ensures transparency.
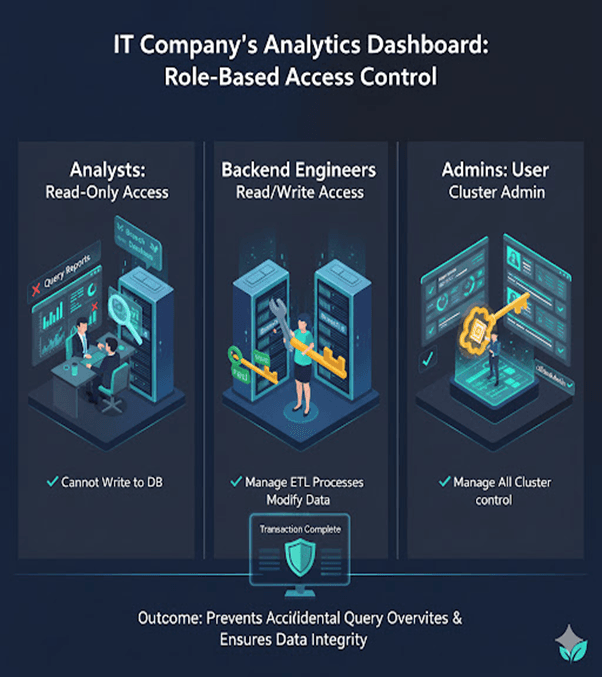
3. IT Company’s Analytics Dashboard
Analysts use a read-only role to query reports.
Backend engineers use readWrite to manage ETL processes.
Admins oversee all users using clusterAdmin roles.
Outcome: Prevents accidental query overwrites during data analysis.
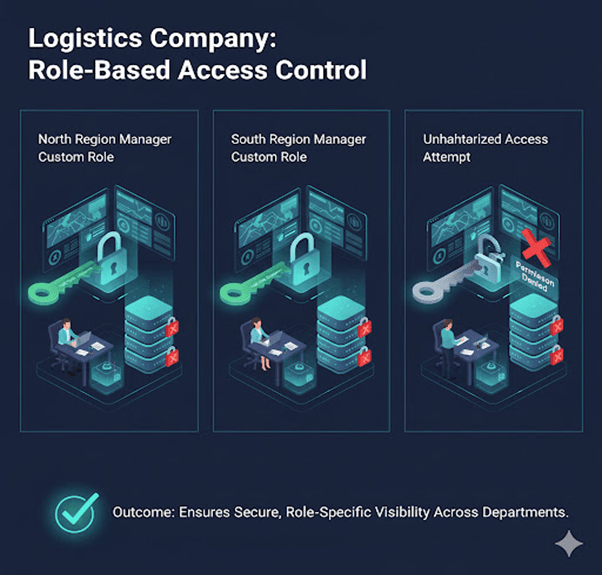
4. Logistics Company
Regional managers have custom roles to view shipments only in their assigned regions.
Outcome: Ensures secure, role-specific visibility across departments.
Module 1: Mongo DB Security Essentials
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI System Design
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
