Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Enabling Authorization
Last Updated: 13th February, 2026Introduction
Imagine setting up your MongoDB database for a new application. Everything works smoothly — inserts, queries, updates.
But then you realize something alarming:
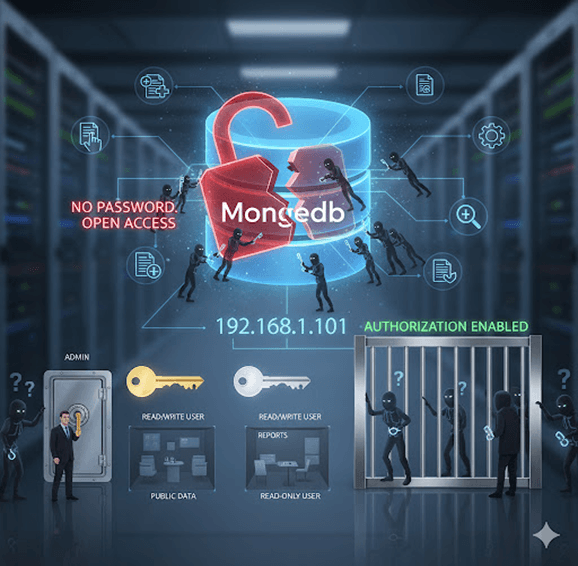
Anyone who knows your server’s IP can access your entire database without a password.
By default, MongoDB starts without authentication or authorization enabled. It assumes a trusted environment — which is risky in today’s cloud-first world.
That’s why authorization becomes your first line of defense in MongoDB security.
What You’ll Learn in This Lesson
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
Enable authorization in MongoDB configuration
Create secure admin users
Assign appropriate roles
Restrict read/write/manage permissions
Think of it like assigning keys in a secure building — not everyone should have access to the vault.
By enabling authorization, you transform your MongoDB instance from an open house into a secure, access-controlled system.
Step 1: Enable Authorization
By default, MongoDB allows open access. To secure your instance, you must explicitly enable authorization.
Update MongoDB Configuration
Edit your configuration file:
# /etc/mongod.conf security: authorization: enabled
Restart MongoDB
sudo systemctl restart mongod
Once restarted, MongoDB will require authentication for all operations.
Step 2: Create an Admin User
After enabling authorization, create a secure administrator account.
use admin db.createUser({ user: "admin", pwd: "StrongPassword123!", roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ] })
What This Does
Creates a user named admin
Assigns a strong password
Grants userAdminAnyDatabase role
Allows managing users across databases
Important: Always use a strong, unique password in production environments.
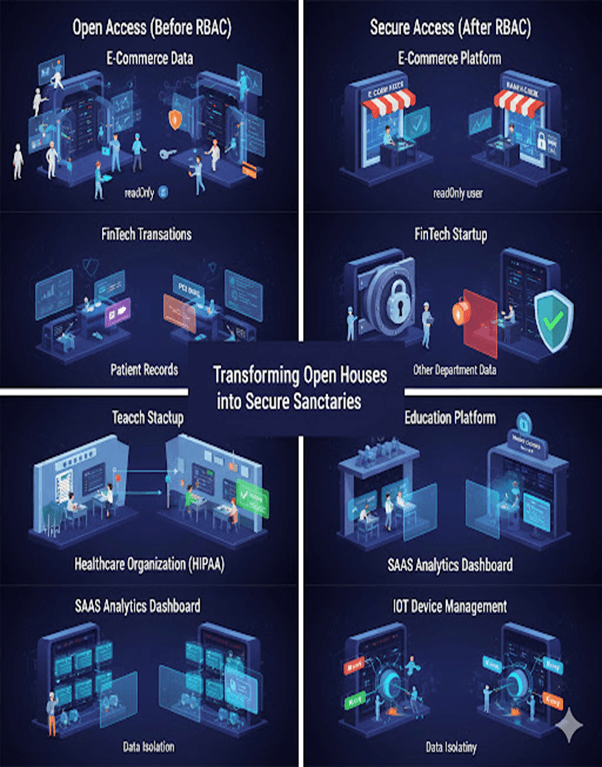
Real-World Use Cases
Below are examples of how enabling authorization protects organizations across industries.
1. E-Commerce Company – Protecting Customer Data
An online store storing millions of customer records including names, emails, and purchase history.
Before:
Developers accessed the database directly
High risk of accidental deletion or unauthorized access
After:
Created role-based access:
readOnly → Analysts
readWrite → Developers
dbAdmin → DevOps
Outcome:
Prevented accidental data loss
Blocked unauthorized access
Improved internal data governance
2. FinTech Startup – Managing Transactions
A digital wallet app storing transaction data and balances.
Risk:
Anyone with network access could query financial data.
Solution:
Enabled authorization
Implemented Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Used strong admin credentials
Outcome:
Restricted access to financial collections
Achieved compliance with standards like PCI DSS
3. Healthcare Organization – Protecting Patient Records
A hospital storing sensitive patient data.
Requirement:
Comply with HIPAA regulations.
Implementation:
Enabled authorization
Assigned role-based access
Doctors could access only their patients’ records
Outcome:
Protected patient privacy
Prevented cross-department data leaks
4. Education Platform – Multi-Level Access
An EdTech platform storing student progress and grades.
Role Structure:
Teachers → Read/Write access
Students → Read-only access
Admins → Full database control
Outcome:
Prevented data tampering
Maintained transparency
5. SaaS Analytics Dashboard – Multi-Tenant Security
A B2B SaaS platform hosting multiple clients on shared MongoDB infrastructure.
Challenge:
Prevent one client from accessing another’s data.
Solution:
Enabled authorization
Separated users by role and database
Outcome:
Strong data isolation
Increased customer trust
6. IoT Device Management System
A smart home startup collecting IoT device data.
Initial Risk:
Devices pushed data without authentication.
Improvement:
Enabled authorization
Assigned each device:
Unique key
Limited insert-only privileges
Outcome:
Prevented malicious data injection
Reduced attack surface
Key Takeaways
MongoDB does not enable authorization by default
Open databases are a major security risk
Enabling authorization protects against:
Unauthorized access
Accidental deletions
Insider threats
Compliance violations
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures:
Users only access what they need
The principle of least privilege is enforced
Final Thought
Security is not optional.
Enabling authorization is the first and most critical step in securing your MongoDB deployment.
Without it, your database remains exposed.
With it, you establish a foundation of trust, control, and compliance.
Module 1: Mongo DB Security Essentials
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI System Design
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
