Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Implementation using Python
Last Updated: 13th February, 2026Imagine you’re a doctor storing patient details in MongoDB — names, addresses, diagnoses, prescriptions.
You secure the database, enable TLS, and even encrypt data at rest. Everything seems safe… right?
But here’s the catch: even with all that, anyone with access to the database (like a DBA or internal staff) can still see your data in plaintext.
This is where Client-Side Field-Level Encryption (CSFLE) comes in.
Instead of letting MongoDB handle encryption, your application encrypts sensitive fields before sending data to the database. MongoDB never sees the raw data — it only stores ciphertext.
So even if the database is breached, hackers get encrypted fields that are impossible to decode without the key.
In This Lesson, You’ll Learn
What Client-Side Field-Level Encryption is
How to implement it using Python and PyMongo
How to configure encryption keys and encrypt specific fields (like credit card numbers or SSNs)
By the end, you’ll be able to make your app a data guardian, ensuring privacy before data even touches MongoDB.
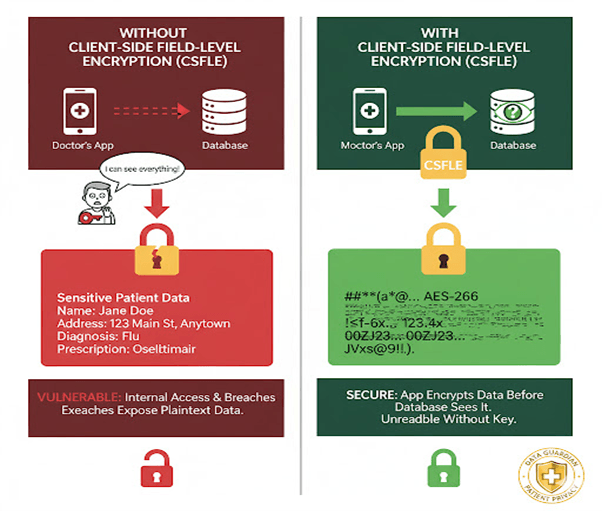
What Is Client-Side Field-Level Encryption (CSFLE)?
Client-Side Encryption (CSE) means data is encrypted and decrypted by the client application, not MongoDB.
Only specific fields (like ssn, creditCard, or salary) are encrypted.
MongoDB only stores encrypted blobs, not the plaintext values.
This ensures even administrators or attackers with database access cannot read sensitive data.
Key Features
End-to-end encryption for specific fields
Keys stored securely outside MongoDB (like in AWS KMS or locally)
Automatic encryption/decryption via a MongoDB driver
Setting Up Python for Field-Level Encryption
Step 1: Install Required Packages
pip install pymongo pymongocrypt
Step 2: Import Dependencies
from pymongo import MongoClient from pymongo.encryption import ClientEncryption from bson.codec_options import CodecOptions from bson import Binary import os
Step 3: Create a Local Master Key
The master key encrypts data encryption keys (DEKs).
master_key = os.urandom(96) with open("master-key.bin", "wb") as f: f.write(master_key)
Step 4: Define KMS Providers
For simplicity, let’s use a local key provider.
kms_providers = { "local": {"key": open("master-key.bin", "rb").read()} }
Step 5: Connect to MongoDB and Create Encryption Key
client = MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017") key_vault_namespace = "encryption.__keyVault" key_vault = client.encryption.__keyVault client_encryption = ClientEncryption( kms_providers, key_vault_namespace, client, CodecOptions() ) data_key_id = client_encryption.create_data_key("local") print("Data Key ID:", data_key_id)
Step 6: Encrypt a Sensitive Field
Let’s encrypt a customer’s credit card number.
encrypted_cc = client_encryption.encrypt( "4111-1111-1111-1111", algorithm="AEAD_AES_256_CBC_HMAC_SHA_512-Deterministic", key_id=data_key_id ) collection = client.secureDB.customers collection.insert_one({ "name": "John Doe", "creditCard": encrypted_cc })
Now the creditCard field is stored encrypted in MongoDB.
Step 7: Decrypt the Field When Reading Data
doc = collection.find_one({"name": "John Doe"}) decrypted_cc = client_encryption.decrypt(doc["creditCard"]) print("Decrypted Credit Card:", decrypted_cc)
Real-Life Examples
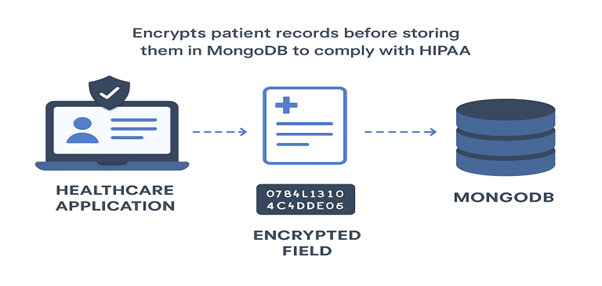
1. Healthcare Application
Encrypts patient records before storing them in MongoDB to comply with HIPAA.
Outcome: Even database admins can’t access patient health details.
2. Banking & Finance
Encrypts credit card and transaction fields using client-side keys managed in AWS KMS.
Outcome: Achieves PCI-DSS compliance and zero-trust security.
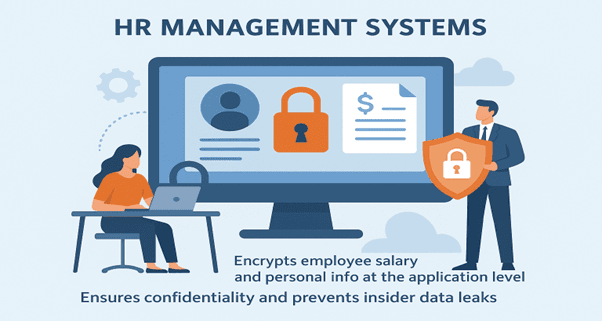
3. HR Management Systems
Encrypts employee salary and personal info at the application level.
Outcome: Ensures confidentiality and prevents insider data leaks.
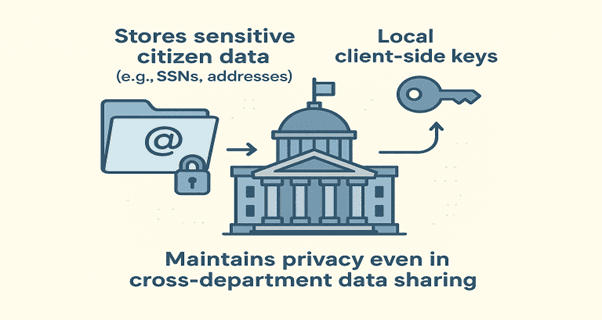
4. Government Systems
Stores sensitive citizen data (e.g., SSNs, addresses) with local client-side keys.
Outcome: Maintains privacy even in cross-department data sharing.

Module 3: Field Level Encryption
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI System Design
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
