Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Using the Encrypted Storage Engine
Last Updated: 13th February, 2026Introduction
Imagine locking your office door every night but leaving all your confidential files unsealed on the desk. Even though no one can walk in easily, if they somehow do, they can still read everything.
That’s exactly what happens when you secure MongoDB with authentication but don’t encrypt your stored data. If someone gains access to your database files or disks, they can directly extract raw information — customer details, transactions, passwords — without ever logging in.
That’s where Encryption at Rest comes in. It ensures that data stored on disk is unreadable to anyone who doesn’t have the encryption key. Even if attackers get the physical files, all they’ll see is encrypted data.
In This Lesson, You’ll Learn:
What encryption at rest means in MongoDB
How to enable the Encrypted Storage Engine (AES-256)
How to create and manage encryption keys securely
By the end, your MongoDB instance will be like a vault — even if someone breaks in, they won’t get the gold.
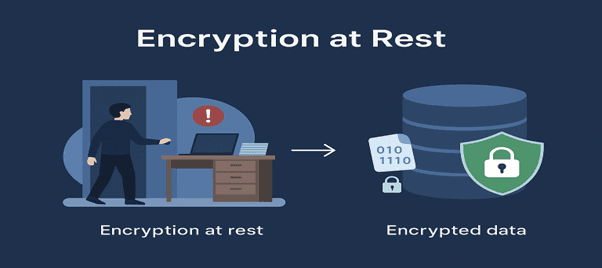
What Is Encryption at Rest?
Encryption at Rest means encrypting data when it is stored on disk — including collections, indexes, and metadata.
MongoDB uses the Encrypted Storage Engine, which performs encryption and decryption automatically during read/write operations.
Key Idea:
Data stays encrypted on disk but is transparently decrypted when accessed by authorized applications.
Enabling Encryption at Rest in MongoDB
Step 1: Create an Encryption Key
This key will be used by MongoDB to encrypt your stored data.
openssl rand -base64 32 > /etc/mongodb-keyfile chmod 600 /etc/mongodb-keyfile chown mongodb:mongodb /etc/mongodb-keyfile
Step 2: Enable Encryption in the Configuration File
Edit your mongod.conf file:
security: enableEncryption: true encryptionKeyFile: /etc/mongodb-keyfile
Step 3: Restart MongoDB
sudo systemctl restart mongod
Now, all your database files on disk are encrypted using AES-256.
Verifying Encryption
You can check if encryption is enabled:
db.serverStatus().encryptionAtRest
If successful, you’ll see output confirming encryption is active.
Real-Life Examples
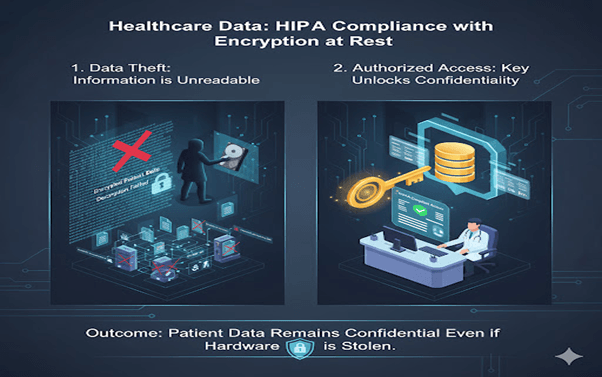
1. Healthcare Records
A hospital stores patient medical histories in MongoDB. To comply with HIPAA, they enable encryption at rest so that stolen drives or backups reveal nothing without the encryption key.
Outcome:
Patient data remains confidential even in case of hardware theft.
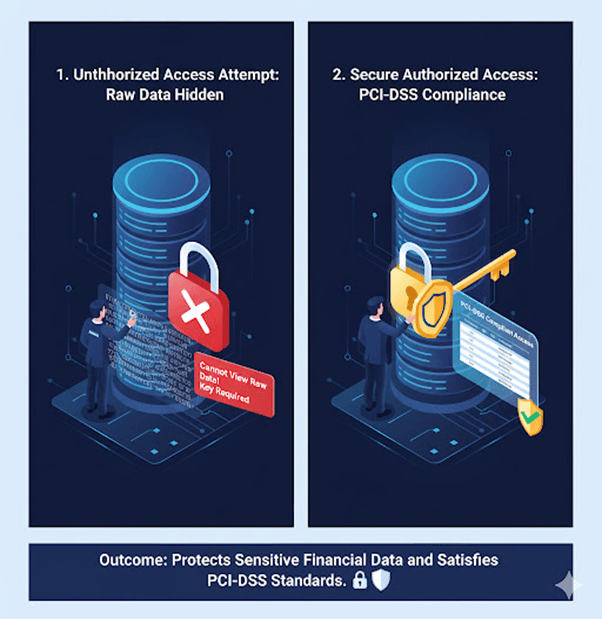
2. Banking and FinTech
A payment gateway uses MongoDB for transaction logs. By enabling encryption at rest, even database administrators can’t view raw data without proper authorization.
Outcome:
Protects sensitive financial data and satisfies PCI-DSS standards.
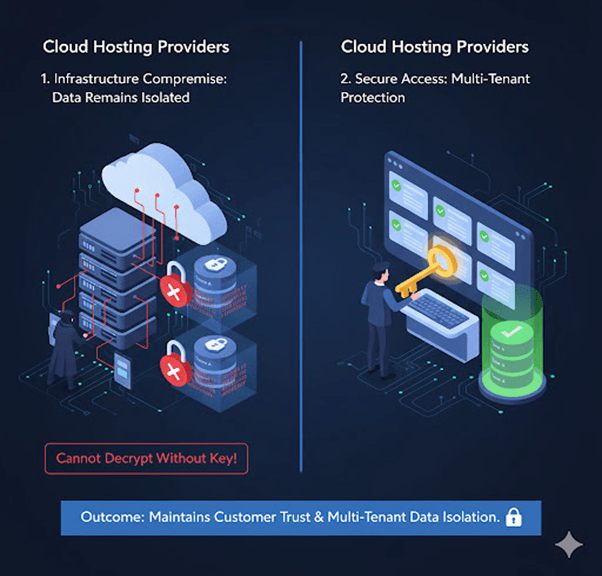
3. Cloud Hosting Providers
A SaaS company hosts MongoDB in multiple virtual machines. Encryption at rest ensures that even if cloud infrastructure is compromised, tenant data stays unreadable.
Outcome:
Maintains customer trust and multi-tenant data isolation.
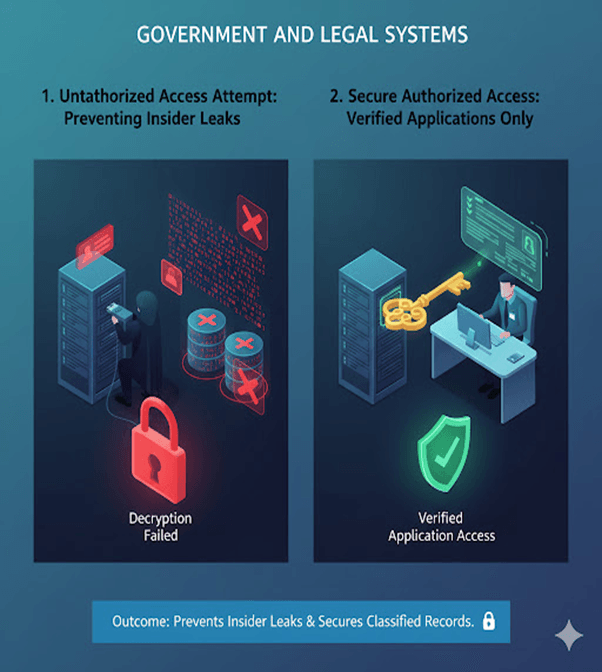
4. Government and Legal Systems
Sensitive legal documents and citizen records are encrypted on disk, ensuring that only verified applications can read or decrypt them.
Outcome:
Prevents insider leaks and secures classified records.
Module 2: Data Encryption Techniques
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI System Design
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
