Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Deployment Architectures
Last Updated: 30th January, 2026In this chapter, we focus on different deployment architectures that determine how models are hosted, accessed, and scaled. Choosing the right architecture impacts reliability, scalability, cost, and maintenance. We will explore on-premise versus cloud deployment, microservices-based deployment, and serverless deployment approaches, highlighting their strengths, weaknesses, and real-world applications. By the end of this chapter, you will understand how deployment architecture shapes the performance and usability of your ML models.
On-Premise vs Cloud Deployment
Machine learning models can be deployed either on-premise or on the cloud. Each approach has its own advantages and trade-offs:
1. On-Premise Deployment:
- The model is hosted on servers physically located within an organization’s infrastructure.
- Common in environments where data privacy, security, or regulatory compliance is critical.
- Gives organizations full control over hardware and resources.
Advantages:
- Full control over data, infrastructure, and security.
- No dependency on internet connectivity for serving predictions.
Challenges:
- High upfront costs for hardware, servers, and maintenance.
- Scaling requires manual setup and additional resources.
- Upgrades and updates can be slower.
Example: A hospital hosting a diagnostic model within its own secure network to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations.
2. Cloud Deployment:
The model is hosted on cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure.
Popular due to ease of scaling, low upfront costs, and managed infrastructure.
Advantages:
Quick setup with minimal hardware requirements.
Easy to scale with demand using cloud-managed services.
Access to additional tools like monitoring, logging, and automated scaling.
Challenges:
Dependence on internet connectivity.
Ongoing operational costs.
Potential data privacy concerns if sensitive data is sent to the cloud.
Example: An e-commerce recommendation model deployed on AWS to serve millions of users globally with low latency.
Microservices Architecture for ML
Microservices architecture is a modern approach where different components of an application are split into independent services. In ML, this often means separating:
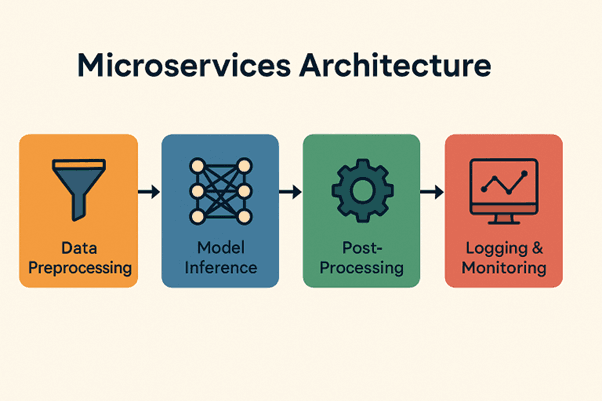
- Data preprocessing
-Model inference
- Post-processing
- Logging and monitoring
Advantages:
Scalability: Each service can scale independently based on demand.
Flexibility: Easier to update, replace, or improve individual components without affecting the entire system.
Fault Isolation: Failures in one service do not crash the entire system.
Example: A recommendation engine might have separate services for:
- Collecting user behavior data
- Generating recommendations using the ML model
- Serving results through an API to the website
Challenges:
- More complex to implement compared to monolithic architectures.
- Requires orchestration tools like Docker Compose or Kubernetes.
Serverless Deployment
Serverless deployment abstracts server management from the developer. Platforms like AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, or Azure Functions handle infrastructure, scaling, and execution, allowing you to focus purely on the model logic.
Advantages:
- No server management required.
- Automatic scaling based on requests.
- Cost-effective: pay only for the compute used.
Challenges:
- Limited execution time (function timeouts).
- Not suitable for long-running or resource-intensive models.
- Cold start latency can impact response time for infrequent requests.
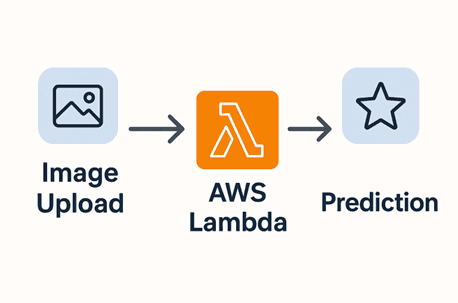
Example: A lightweight image classification model hosted on AWS Lambda that processes images uploaded by users and returns predictions in seconds.
Summary:
Choosing the right deployment architecture is critical for model performance, reliability, and scalability.
On-premise deployment provides full control and security but requires significant resources.
Cloud deployment is scalable, flexible, and managed but introduces ongoing costs and potential privacy concerns.
Microservices architecture allows modular, scalable, and maintainable ML systems.
Serverless deployment abstracts infrastructure, enabling quick and cost-effective deployment for lightweight models.
Module 2: Deployment Architectures and Tools
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
