Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Handling Model Maintenance and Updates
Last Updated: 30th January, 2026Once deployed, models need continuous maintenance to remain accurate and effective. This chapter covers strategies for retraining models, handling data drift, automating updates, and ensuring long-term reliability. You’ll learn how to monitor model performance, schedule retraining, and implement alerts, ensuring that your deployment remains robust even as data and user behavior evolve.
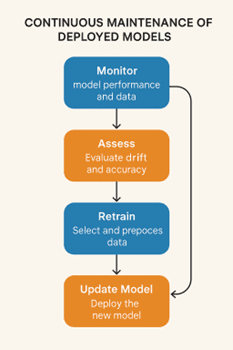
Detecting Data Drift
Data drift occurs when the statistical properties of incoming data change over time, leading to degraded model performance. For example, a model trained on customer behavior last year may not perform well today if user preferences or demographics have shifted. Detecting drift early is crucial for maintaining model accuracy and reliability.
Strategies to Detect Data Drift:
1. Compare Summary Statistics:
- Calculate mean, median, standard deviation, and distributions for key features.
- Compare these statistics between new incoming data and the original training data.
Example: If the average purchase amount has significantly increased compared to training data, it may indicate drift.
2. Monitor Prediction Distributions:
- Track how model predictions are changing over time.
- Sudden spikes or drops in predicted classes or regression outputs may indicate drift.
3. Automated Alerts for Anomalies:
- Implement monitoring pipelines that trigger alerts when drift metrics exceed thresholds.
Example: A sudden 20% drop in model accuracy triggers a notification to the ML team.
Practical Example:
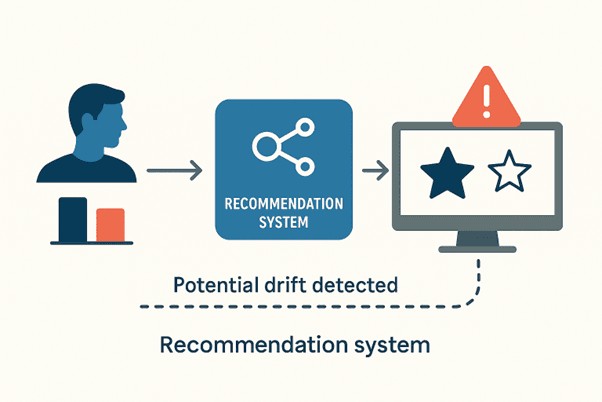
A recommendation system trained on last year’s seasonal trends may underperform if user behavior changes due to a new holiday trend or product launch.
By monitoring input features and output predictions, the system can flag potential drift, prompting retraining or adjustment.
Best Practices:
- Track both input features and model outputs.
- Use visualization tools like dashboards to quickly identify trends.
- Maintain a historical log of input data and predictions for comparison.
Automating Retraining
Models degrade over time if they are not updated to reflect new data patterns. Automating retraining ensures models stay accurate without manual intervention.
Key Steps to Automate Retraining:
1. Schedule Retraining Pipelines:
Use batch jobs or cron jobs to retrain models periodically.
Example: Retrain a demand forecasting model every night using the day’s sales data.
2. Integrate CI/CD Pipelines:
- Automatically test and validate newly trained models before deployment.
- If the new model performs better, it replaces the old one seamlessly.
3. Monitor Model Performance:
- Evaluate metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, or RMSE after each retraining cycle.
- Ensure performance is improving or at least consistent.
Practical Example:
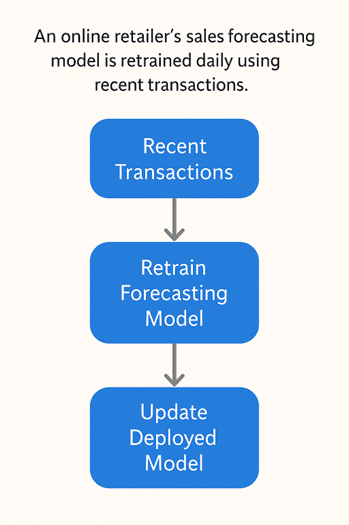
- An online retailer’s sales forecasting model is retrained daily using recent transactions.
- This ensures predictions reflect current trends, such as seasonal spikes or promotional campaigns.
- The retraining pipeline automatically updates the deployed model with minimal human intervention.
Best Practices:
- Keep a backup of previous model versions for rollback.
- Monitor model drift and performance post-retraining to avoid deploying a degraded model.
- Maintain automation logs for debugging and auditing.
Security and Compliance
Deploying models in production involves handling sensitive data, which requires strong security and compliance measures. Ignoring these can lead to data breaches, legal issues, and loss of trust.
Key Areas to Focus On:
Data Privacy:
- Encrypt all sensitive input and output data.
- Mask personally identifiable information (PII) when storing logs.
Secure APIs:
- Use HTTPS to encrypt communication between clients and servers.
- Implement authentication and authorization (e.g., API tokens, OAuth).
Regulatory Compliance:
- Follow guidelines such as GDPR (EU), HIPAA (healthcare), or CCPA (California) for data handling.
- Maintain audit trails of all model predictions and requests.
Practical Best Practices:
- Token-Based Authentication: Ensure only authorized users or systems can access your API.
- Audit Logs: Log inputs, outputs, and user requests to detect misuse or anomalies.
- Periodic Security Audits: Test APIs and deployment infrastructure for vulnerabilities.
Example Scenario:
A healthcare prediction model deployed for patient risk assessment must encrypt all patient data, log every prediction, and ensure only authorized personnel can access the API. This protects privacy and meets compliance standards.

Module 4: Best Practices, MLOps, and Real-World Tips
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
