Your Success, Our Mission!
3000+ Careers Transformed.
Popular Tools & Frameworks
Last Updated: 30th January, 2026Choosing the right tools and frameworks is essential for efficient and reliable model deployment. This chapter introduces popular frameworks, libraries, and platforms that make serving machine learning models easier, faster, and scalable. We will explore Flask and FastAPI for building APIs, Docker for containerization, and cloud platforms like AWS, GCP, and Azure for hosting models. By the end, you will understand which tools to use for different deployment scenarios.
Flask / FastAPI
Flask and FastAPI are lightweight Python frameworks commonly used to wrap ML models as APIs, enabling applications to send input data and receive predictions.
Flask:
- A micro web framework for Python that is simple to learn and use.
- Allows you to expose your model via REST endpoints.
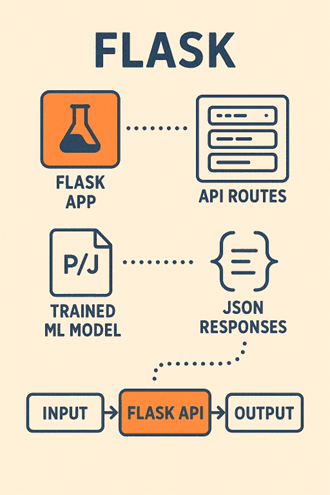
Example Workflow with Flask:
1. Load your trained model using Pickle or Joblib.
2. Define API routes that accept input data.
3. Return model predictions as JSON responses.
Advantages:
- Lightweight and easy to set up.
- Large community support and extensive documentation.
Challenges:
- Synchronous by default, which may limit scalability.
- May require additional setup for production-grade deployments.
FastAPI:
- A modern Python framework optimized for high-performance APIs.
- Supports asynchronous requests natively, enabling better scalability.
- Built-in data validation and automatic documentation using Pydantic and OpenAPI.
Advantages:
- Fast, scalable, and ideal for production-grade APIs.
- Automatic interactive API documentation.
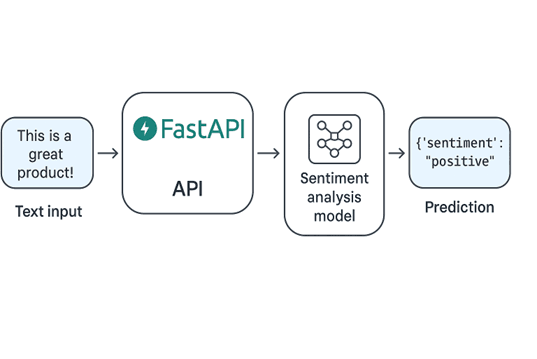
Example Use Case: Deploying a sentiment analysis model where users can send text input and get instant predictions via an API.
Docker & Containerization
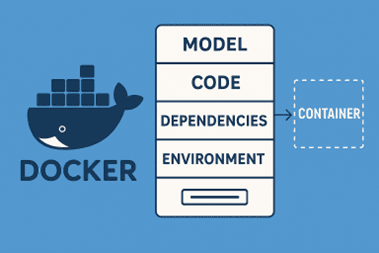
Docker is a tool that allows you to package your ML model, code, dependencies, and environment into a container. This ensures that the model runs consistently across different machines or cloud platforms.
Why use Docker:
- Eliminates environment mismatch issues (e.g., library versions).
- Simplifies deployment and scaling.
- Works seamlessly with cloud and orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
Example Workflow:
- Write a Dockerfile specifying Python version, dependencies, and the API script.
- Build a Docker image containing your model and API.
- Run a Docker container locally or deploy to a cloud server.
Advantages:
- Consistent environment across development, testing, and production.
- Easier to scale and manage.
- Supports both microservices and monolithic architectures.
Challenges:
- Adds a slight learning curve for beginners.
- Containers consume system resources; optimization may be needed for large models.
Cloud Platforms (AWS, GCP, Azure)
Cloud platforms provide managed services for deploying and serving ML models, abstracting away server management and infrastructure concerns.
AWS (Amazon Web Services):
- Services like SageMaker enable training, deploying, and monitoring models.
- Offers REST endpoints, automatic scaling, and integrated security.
GCP (Google Cloud Platform):
- AI Platform supports model deployment with versioning, monitoring, and batch predictions.
- Integrates with other Google services like BigQuery for seamless data pipelines.
Azure:
- Azure ML provides deployment tools for real-time and batch inference.
- Offers automatic scaling, monitoring, and MLOps support.
Advantages of Cloud Platforms:
- Quick setup and deployment.
- Handles scaling automatically.
- Built-in monitoring, logging, and security features.
Challenges:
- Ongoing operational costs.
- Requires internet connectivity.
- Sensitive data may require careful compliance management.
Example:
A company wants to deploy a deep learning image classifier globally. Using AWS SageMaker, the model can be deployed with a REST API, auto-scaling to handle thousands of requests per second.
Summary:
- Flask and FastAPI help create APIs for serving models with different levels of scalability.
- Docker ensures consistent environments and simplifies deployment across machines and clouds.
- Cloud platforms like AWS, GCP, and Azure provide managed deployment services, making scaling and monitoring easier.
- Selecting the right combination of tools depends on model complexity, expected traffic, scalability needs, and budget.
Module 2: Deployment Architectures and Tools
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
