Your Success, Our Mission!
6000+ Careers Transformed.
Graph and Tree Algorithms
Last Updated: 2nd February, 2026Graph and tree algorithms are methods to traverse, search, and analyze hierarchical or networked data structures. Tree algorithms include traversals like in-order, pre-order, and post-order. Graph algorithms cover BFS, DFS, Dijkstra, and Prim’s for shortest paths, connectivity, and spanning trees, widely used in networks, maps, and data processing.
Breadth-First Search (BFS) Algorithm
Breadth-First Search (BFS) is a graph traversal algorithm that explores nodes level by level, starting from a given source node. It uses a queue to keep track of nodes to visit next, ensuring that all neighbors of a node are visited before moving deeper.
In Python, BFS can be implemented using a queue from collections.deque. The main operations performed in BFS are:
- Enqueue: Add the starting node to the queue.
- Visit: Dequeue a node, process it, and enqueue all unvisited neighbors.
- Mark Visited: Keep track of visited nodes to avoid cycles.
- Repeat: Continue until the queue is empty.
BFS is widely used in finding the shortest path in unweighted graphs, checking connectivity, social network analysis, and maze or puzzle solving.
Time Complexity: O(V + E), where V is vertices and E is edges.
Example:
Input:
from collections import deque def bfs(graph, start): visited = set() queue = deque([start]) while queue: node = queue.popleft() if node not in visited: print(node, end=" ") visited.add(node) queue.extend([n for n in graph[node] if n not in visited]) graph = { 'A': ['B','C'], 'B': ['D','E'], 'C': ['F'], 'D': [], 'E': ['F'], 'F': [] } print("BFS Traversal:", end=" ") bfs(graph, 'A')
Output:
BFS Traversal: A B C D E F
Graphical Representation of Breadth-First Search Algorithm
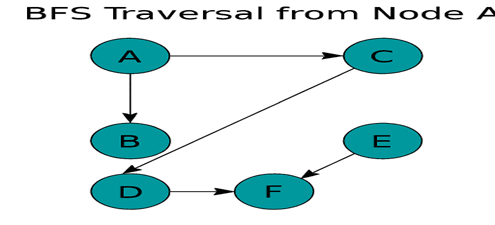
Depth-First Search (DFS) Algorithm
Depth-First Search (DFS) is a graph traversal algorithm that explores as deep as possible along each branch before backtracking. It uses a stack or recursion to keep track of visited nodes, ensuring that each path is fully explored before moving to the next.
In Python, DFS can be implemented using recursion or an explicit stack. The main operations performed in DFS are:
- Visit: Start from a node and mark it as visited.
- Explore: Recursively or iteratively visit unvisited neighbors.
- Backtrack: Return to the previous node when no unvisited neighbors remain.
- Repeat: Continue until all reachable nodes are visited.
DFS is widely used in pathfinding, puzzle solving, cycle detection, topological sorting, and exploring all possible configurations in graphs.
Time Complexity: O(V + E), where V is vertices and E is edges.
Example:
Input:
def dfs(graph, node, visited=None): if visited is None: visited = set() visited.add(node) print(node, end=" ") for neighbor in graph[node]: if neighbor not in visited: dfs(graph, neighbor, visited) graph = { 'A': ['B','C'], 'B': ['D','E'], 'C': ['F'], 'D': [], 'E': ['F'], 'F': [] } print("DFS Traversal:", end=" ") dfs(graph, 'A')
Output:
DFS Traversal: A B D E F C
Graphical Representation of Depth - First Search Traversal Algorithm
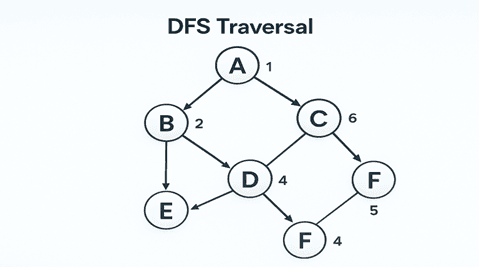
Dijkstra Algorithm
Dijkstra’s algorithm is used to find the shortest path from a source node to all other nodes in a weighted graph with non-negative edge weights. It repeatedly selects the node with the smallest tentative distance, updates the distances of its neighbors, and uses a priority queue for efficiency.
In Python, Dijkstra’s algorithm can be implemented using a min-heap (priority queue) from heapq. The main operations performed in Dijkstra’s algorithm are:
- Initialize: Set the distance of the source node to 0 and all others to infinity.
- Select Node: Choose the unvisited node with the smallest tentative distance.
- Update Distances: For each neighbor, calculate and update the shortest distance.
- Mark Visited: Once all neighbors are processed, mark the node as visited.
- Repeat: Continue until all nodes have been visited.
Dijkstra’s algorithm is widely used in routing algorithms, GPS navigation, network optimization, and shortest path calculations in weighted graphs.
Time Complexity: O((V + E) log V) using a priority queue.
Example:
Input:
def dijkstra(graph, start): nodes = list(graph.keys()) dist = {node: float('inf') for node in nodes} dist[start] = 0 visited = set() while nodes: u = min((n for n in nodes if n not in visited), key=lambda x: dist[x], default=None) if u is None: break visited.add(u) for v, w in graph[u].items(): if dist[u] + w < dist[v]: dist[v] = dist[u] + w return dist graph = { 'A': {'B':1, 'C':4}, 'B': {'C':2, 'D':5}, 'C': {'D':1}, 'D': {} } print("Shortest distances from A:", dijkstra(graph, 'A'))
Output:
Shortest distances from A: {'A': 0, 'B': 1, 'C': 3, 'D': 4}
Graphical Representation of Dijkstra Algorithm
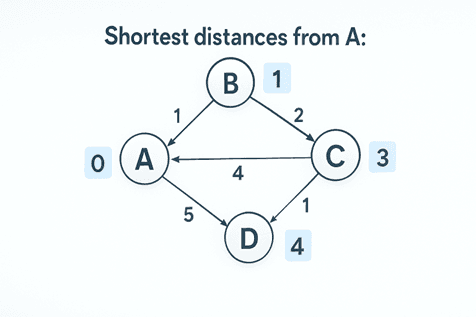
Prim’s Algorithm
Prim’s Algorithm constructs a Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) of a weighted graph by repeatedly selecting the smallest edge that connects a visited node to an unvisited node. It starts from any node and gradually grows the MST until all nodes are included.
In Python, Prim’s algorithm can be implemented using a priority queue (min-heap) to efficiently select the minimum edge. The main operations performed in Prim’s algorithm are:
- Start: Choose any node as the starting point of the MST.
- Select Edge: Pick the smallest edge connecting a visited node to an unvisited node.
- Add to MST: Include the selected edge and mark the new node as visited.
- Repeat: Continue until all nodes are included in the MST.
Prim’s algorithm is widely used in network design, connectivity optimization, designing efficient electrical grids, and MST-related problems.
Time Complexity: O(V²) for adjacency matrix or O(E log V) with a priority queue.
Example:
Input:
import sys g=[[0,2,0,6,0],[2,0,3,8,5],[0,3,0,0,7],[6,8,0,0,9],[0,5,7,9,0]] s=[0]+[0]*4;e=0 while e<4: m,a,b=sys.maxsize,0,0 for i in range(5): if s[i]: for j in range(5): if not s[j] and g[i][j] and g[i][j]
Output:
0-1 (2) 1-2 (3) 1-4 (5) 0-3 (6)
Graphical Representation of Prim’s Algorithm
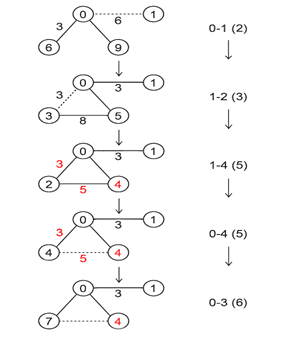
Module 3: Algorithms in Python
Top Tutorials
Related Articles
- Courses
- MS in Computer Science: Machine Learning and AI Engineering
- MS in Computer Science: Cloud Computing with AI System Design
- Professional Fellowship in Data Science and Agentic AI Engineering
- Professional Fellowship in Software Engineering with AI and DevOps
- Advanced Certification in Data Analytics & Gen AI Engineering
- Advanced Certification in Web Development & Gen AI System Design
- Join AlmaBetter
- Sign Up
- Become A Coach
- Coach Login
- Policies
- Privacy Statement
- Terms of Use
- Contact Us
- admissions@almabetter.com
- 08046008400
- Official Address
- 4th floor, 133/2, Janardhan Towers, Residency Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560025
- Communication Address
- Follow Us
© 2026 AlmaBetter
